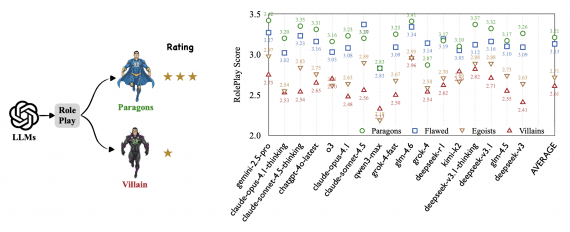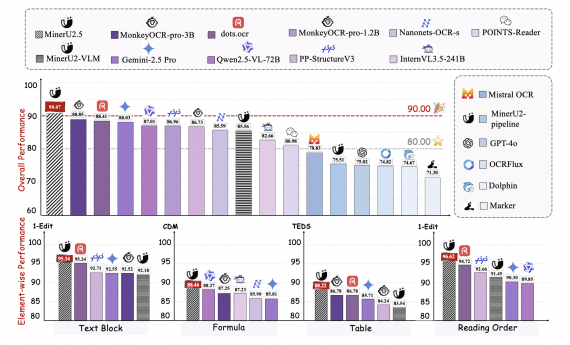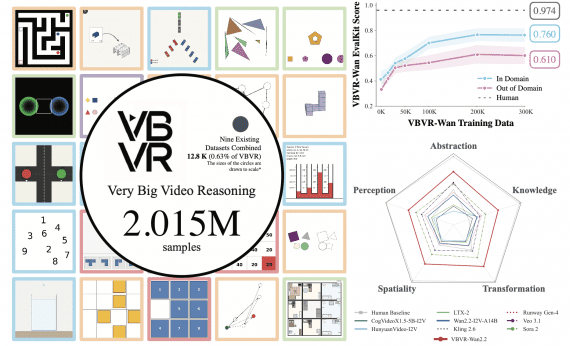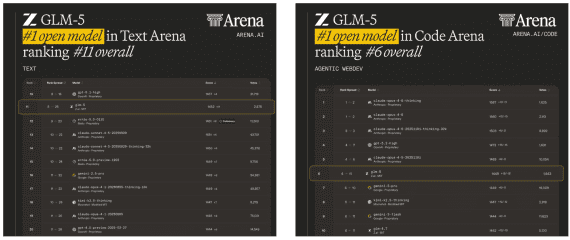
Current academic language models still rely on external Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems, causing undesirable latency in speech synthesis. To address this, the Mini-Omni model introduces an audio-based, end-to-end conversational capability that supports real-time speech interaction without additional TTS systems. This is achieved through a text-instructed speech generation method and batch-parallel strategies during inference, maintaining the original language capabilities of the model with minimal degradation.
The researchers have named this approach “Any Model Can Talk.” QWEN2-0.5b model, equipped with the “Any Model Can Talk” framework, can effectively handle speech tasks while maintaining its original language processing strengths.
The introduction of the VoiceAssistant-400K dataset further fine-tunes models for optimized speech output. To date, Mini-Omni is the first open-source model offering fully end-to-end real-time speech interaction, paving the way for future research in this field.
The project is available on GitHub and Hugging Face.
Key Features
- Real-Time Speech-to-Speech Capabilities: Mini-Omni allows for natural speech conversations, handling both input and output in audio form.
- Simultaneous Text and Audio Generation: The model can “talk while thinking,” generating text and audio simultaneously, ensuring a smooth conversational flow.
- Streaming Audio Output: Mini-Omni supports real-time streaming of audio outputs, making it ideal for interactive applications.
- Batch Inference: The model includes “Audio-to-Text” and “Audio-to-Audio” batch inference methods to further boost performance.
Model Architecture
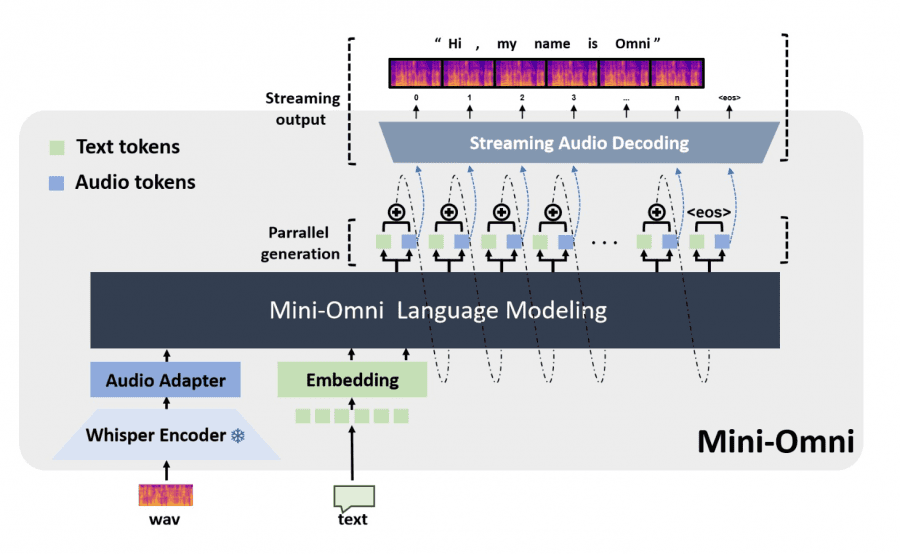
The Mini-Omni model is built on Qwen2-0.5B, a transformer architecture with 24 blocks and an internal dimension of 896. This foundation is enhanced with a Whisper-small encoder to process speech input effectively. This unique combination allows Mini-Omni to integrate real-time audio reasoning into its language processing capabilities.
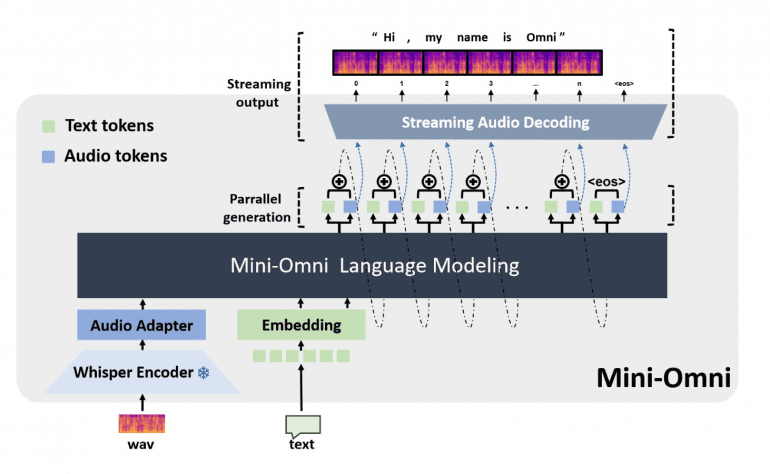
Parallel Text-Audio Generation: Mini-Omni employs a parallel text-audio generation method, using batch parallel decoding to generate speech and text simultaneously. This method ensures that the model can maintain its reasoning capabilities across modalities without compromising performance.
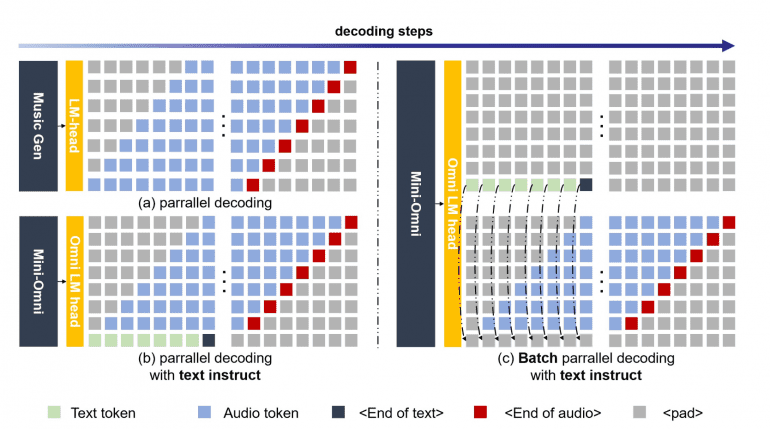
“Any Model Can Talk” Framework
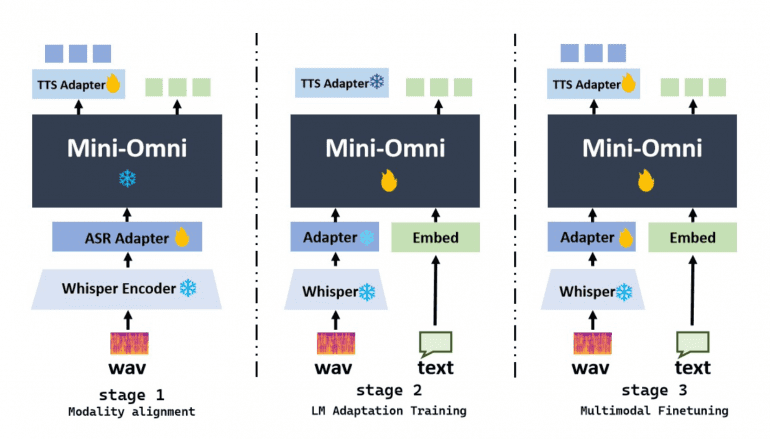
This framework allows existing language models, such as LLaMA, Vicuna, and Baichuan, to adopt speech capabilities with minimal additional training. The process involves three phases: modality alignment, adaptation training, and multimodal fine-tuning, extending the speech interaction capabilities of these models.
Datasets and Training
Mini-Omni was trained on 8,000 hours of speech data and 2 million text-based data points from the Open-Orca dataset. Additionally, the researchers introduced the VoiceAssistant-400K dataset, comprising 400,000 entries specifically designed for fine-tuning speech assistant models.
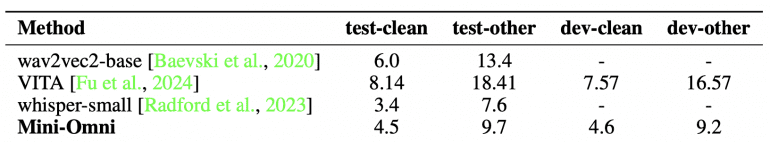
Performance Evaluation
The model demonstrated strong performance in both Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech tasks. For example, it achieved a word error rate (WER) of 4.5% on the LibriSpeech test-clean dataset, closely trailing behind established models like Whisper-small, which achieved 3.4%.
Conclusion
The Mini-Omni model is a pioneering effort in real-time multimodal AI, offering significant advancements in speech interaction capabilities. Its innovative parallel text-audio generation method and the “Any Model Can Talk” framework provide a flexible, efficient way to enhance AI models with speech capabilities, opening new possibilities for real-time, interactive AI applications.