NVIDIA researchers have introduced X-MeshGraphNet, a novel extension of MeshGraphNet that addresses key scalability and practical limitations in physics simulation. The open-source framework, now available through NVIDIA Modulus, enables efficient simulation of complex physical systems while removing the dependency on pre-generated simulation meshes. The code implementation is available through NVIDIA Modulus.
State-of-the-art methods like finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) are computationally expensive. X-MeshGraphNet provides a faster alternative while maintaining accuracy for real-time applications and design optimization.
Model Architecture
The framework extends MeshGraphNet’s capabilities through:
- Custom graph construction directly from CAD files, eliminating mesh generation at inference;
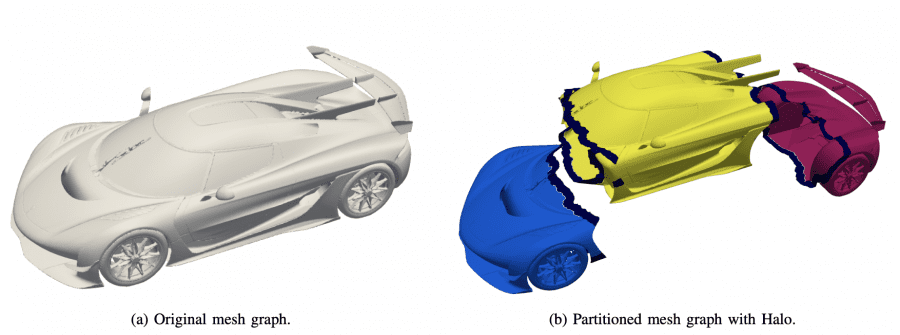
- Graph partitioning with halo regions for scalable processing;
- Multi-scale graph generation for efficient handling of both local and global interactions.
X-MeshGraphNet employs a three-layer system: point cloud generation directly from CAD files with k-nearest neighbor connectionsg, graph partitioning with halo regions enabling seamless message passing, multi-scale representation combining coarse and fine-resolution point clouds
The framework is built on 15 message passing layers, hidden dimension of 256, ReLU activations, and training using bfloat16 precision on H100 GPUs.
X-MeshGraphNet Performance
The researchers validated X-MeshGraphNet’s performance using three representative samples (100, 300, and 500) from the DrivAerML dataset, each featuring different car geometries. The tests demonstrated the model’s consistent accuracy across varying vehicle designs, successfully predicting both pressure distributions and wall shear stress patterns.
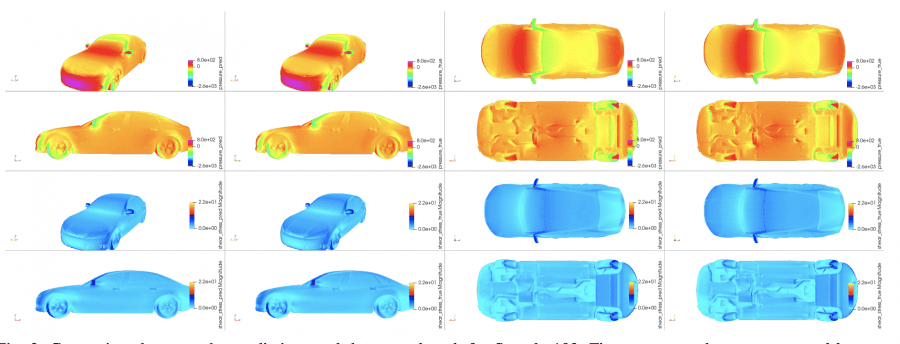
rows show wall shear stress.
The model’s predictions closely matched the ground truth CFD simulations, particularly excelling at capturing high-pressure regions at the front of the vehicles and low-pressure areas around the rear. The model maintained high fidelity in predicting complex aerodynamic features across all three samples, despite their distinct geometric characteristics.
X-MeshGraphNet represents a significant advancement in physics simulation, offering a practical solution for real-time applications while maintaining accuracy. Its integration into NVIDIA Modulus makes it immediately accessible to researchers and practitioners.