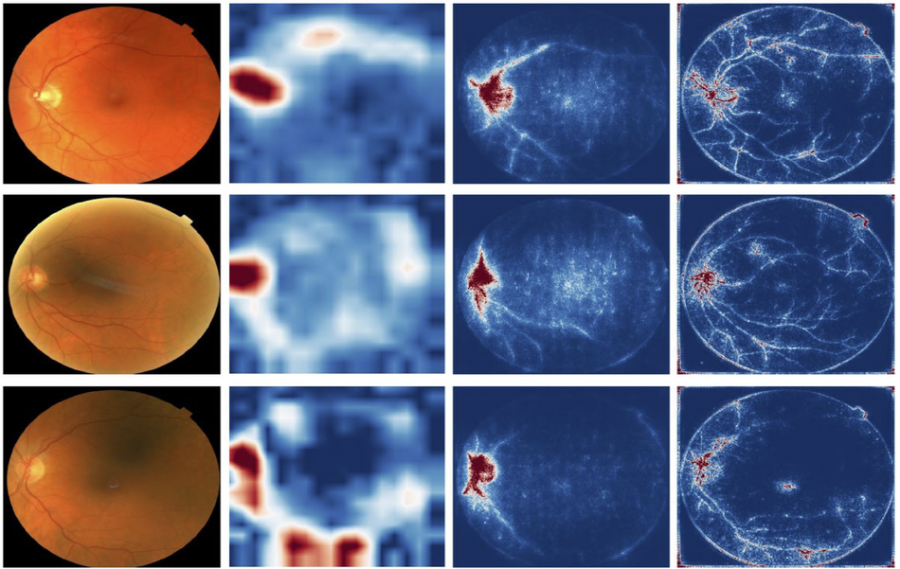
Researchers from Google Health have developed a method that uses deep learning to detect anemia only from the eye.
In their recent paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, researchers describe their findings in using deep learning on photographs from the back of the eye to quantify hemoglobin levels in the blood and consequently detect anomia in patients. In fact, they performed a population-based study to identify areas in the eye that contain signs of anemia. They employed deep learning to analyze the eye image data and discovered that most clues come from the optical disc around the blood vessels in the eye.
In order to validate their model, researchers performed another study where they employ and test their model on a different patient group, namely from the Asian continent. The study confirmed the usability of the model in detecting anemia from eye images.
This research showed how machine learning can be used to support existing methods for anemia detection and can provide a non-invasive screening alternative. Researchers mention that compared to just using metadata, deep learning improved the detection of anemia in terms of classification score (AUC), from 74 percent to 88 percent.
More about the method can be read in the paper.