
Researchers from the University of Cambridge and Google AI have proposed a new image retrieval method that leverages region detection to provide improved image similarity estimates.
In the novel paper, “Detect-to-Retrieve: Efficient Regional Aggregation for Image Search” accepted at CVPR2019 researchers propose to use a trained landmark detector to index image regions and support image retrieval for improved accuracy.
In fact, researchers argue that better aggregated image representation can be obtained detecting specific regions and extracting local visual words in those regions. In order to tackle the problem using this approach, researchers first created a new dataset od landmark bounding boxes based on Google Landmarks dataset.
Then, they used the new dataset and a trained landmark detector to extract information from local regions which is later aggregated into an image representation.
In the paper, the authors also propose a so-called regional aggregated selective match kernel (R-ASMK), that combines the information from different regions and gives a better image representation (from a perspective of image retrieval).
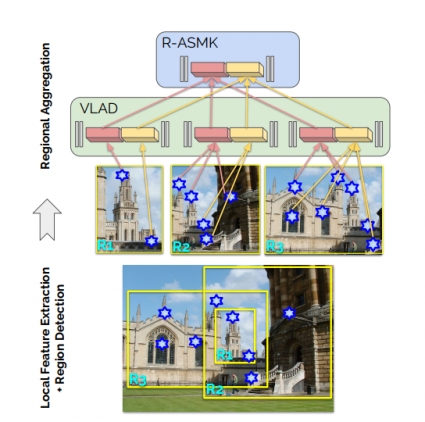
The proposed image retrieval method based on object semantics outperforms current state-of-the-art methods by a large margin on the Revisited Oxford and Paris datasets. Researchers show that regional search improves the accuracy of image retrieval systems, especially in cluttered scenes.
The new dataset and the implementation of the proposed method have been open-sourced and are available on Github.