EzAudio, a new transformer-based text-to-audio (T2A) diffusion model developed by researchers from Tencent AI Lab and Johns Hopkins University. EzAudio addresses key challenges in T2A generation, including generation quality, computational cost, diffusion sampling, and data preparation. EzAudio outperforms current open-source models in both objective metrics and subjective evaluations, making it suitable for applications such as music generation and sound effects. The model demo is available on Hugging Face.
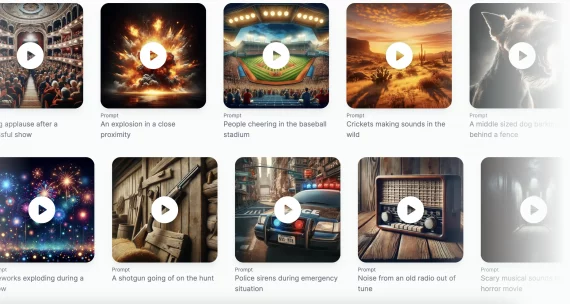
EZaudio samples
“A vehicle engine revving then accelerating at a high rate as a metal surface is whipped followed by tires skidding”:
“A horse clip-clops in a windy rain as thunder cracks in the distance”:
“A piano playing as plastic bonks”:
Model Architecture
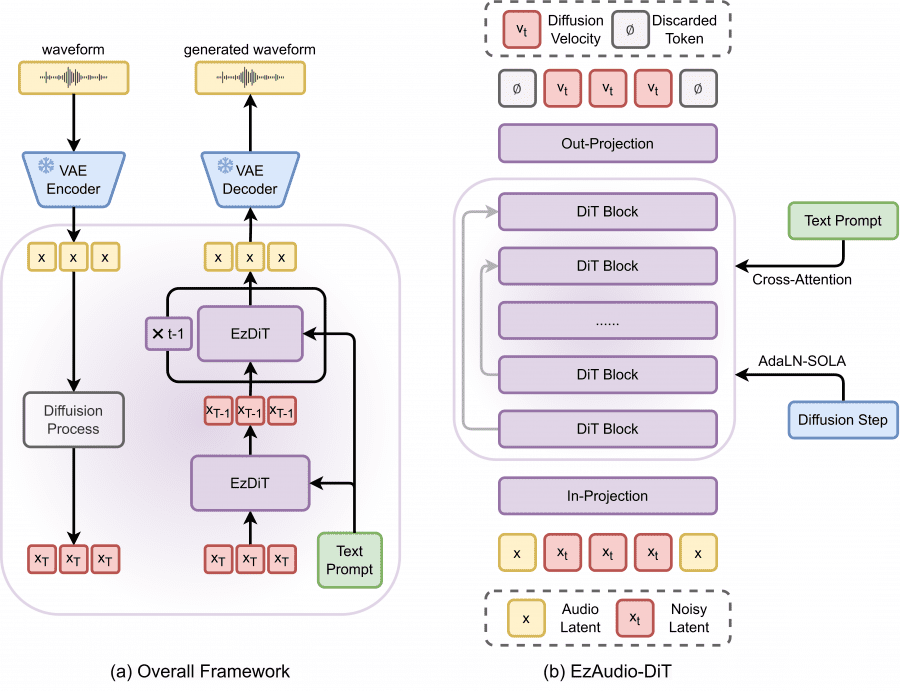
Waveform VAE
EzAudio uses a 1D waveform Variational Autoencoder (VAE) instead of 2D spectrogram representations. This approach avoids the complexities of handling 2D spectrograms and eliminates the need for an additional neural vocoder.
Optimized Diffusion Transformer
The model features a specially designed transformer architecture for audio latent representations and diffusion modeling. • Key innovations include:
- AdaLN-SOLA: A modified adaptive layer normalization technique that reduces parameters while maintaining performance.
- Long-skip connections: Helps retain detailed input information across the transformer.
- RoPE and QK-Norm: Techniques to stabilize training and improve convergence.
Training strategy
Three-stage data-efficient approach includes:
- Masked modeling on unlabeled data for learning acoustic dependencies.
- Text-to-audio alignment learning using synthetic captions.
- Fine-tuning on human-labeled data for precise generation.
Classifier-free guidance (CFG) rescaling improves prompt alignment while preserving audio quality at higher CFG scores. It also eliminates the need to find an optimal CFG score, simplifying the model’s use.
Results
EzAudio-XL achieves a Frechet Distance (FD) of 14.98 and a CLAP score of 0.314, outperforming existing open-source models.
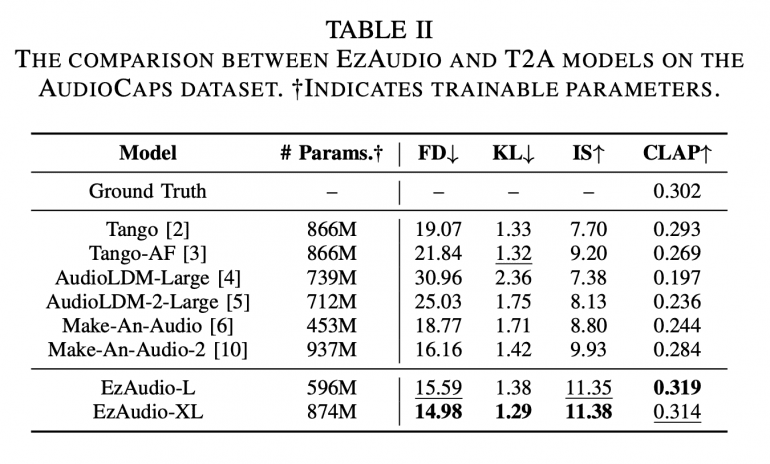
Subjective evaluations show EzAudio-XL approaching the quality of real recordings.
“EzAudio produces highly realistic audio samples, outperforming existing open-source models in both objective and subjective evaluations,” the researchers state in their paper.
The team plans to integrate ControlNet and DreamBooth technologies and explore applications in voice and music generation.
The rapid advancement of latent diffusion-based text-to-image models has paved the way for similar innovations in audio generation. EzAudio builds on this progress, offering a more efficient and higher-quality solution for T2A tasks.