
A group of researchers from the Harbin Engineering University in China has proposed a new method that restores color and removes haze from underwater images.
The novel method, based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) is able to reconstruct underwater clear images in an end-to-end manner while preserving image quality and structural similarity. Researchers proposed a framework where an unsupervised GAN model is used together with an autoencoder network to learn image dehazing and colorization for underwater images.
In fact, within the proposed framework, the Generative Adversarial Network is used to generate realistic synthetic underwater images from in-air images and depth maps. Then, this synthetic data was used to train a U-Net autoencoder model which learns how to perform the actual color restoration and dehazing.
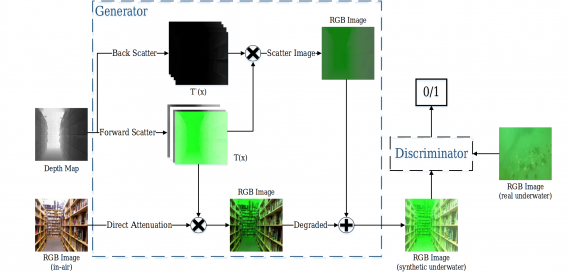
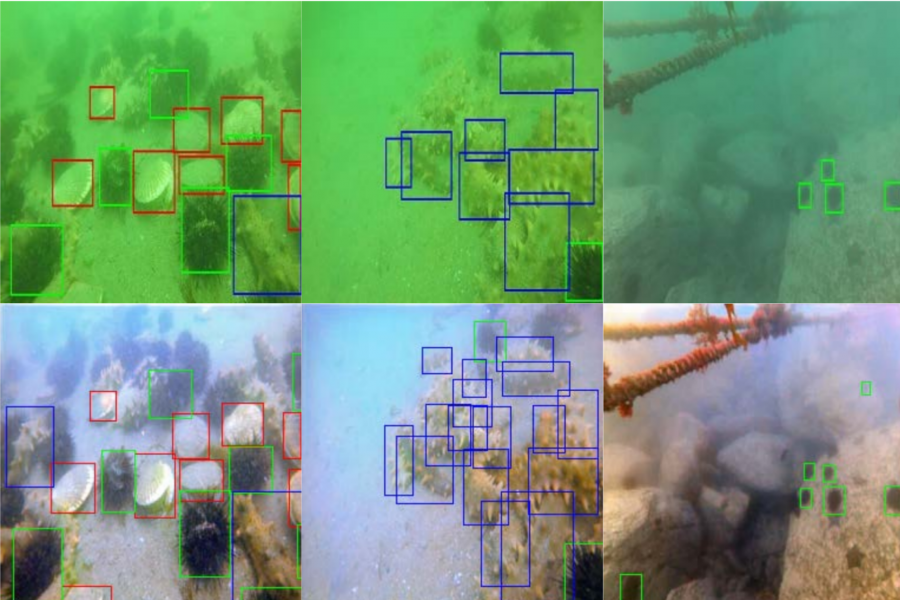
Researchers evaluated the proposed method both quantitatively and qualitatively. The GAN model, or so-called “underwater GAN” or UWGAN, was trained to generate underwater-style images using the NYU-Depth Dataset. The results were compared against existing methods for color restoration starting with Histogram Equalization all the way to more complex methods based on neural networks. According to researchers and the evaluation results, the method performs well and is able to reconstruct clear images.
More details about the method can be found in the paper. Researchers open-sourced the implementation of the method and it is available on Github.