A research team from the Chinese company Baichuan has introduced Baichuan-M3 — an open medical language model that, instead of the traditional question-and-answer mode, conducts a full clinical dialogue, actively gathering medical history and making informed medical decisions. Models and weights are available on Hugging Face, and the source code for the evaluation platform along with example projects are published on GitHub under the commercial Apache 2.0 license.
The Next Step in Medical AI
Imagine a typical scenario: you come to a doctor complaining of a headache. An ordinary medical AI model will simply produce a ready list of possible causes and standard recommendations. Baichuan-M3, however, will behave like an experienced physician — it will methodically clarify details: exactly when the pain started, what its character is, whether there are accompanying symptoms, what medications you are taking, whether similar episodes have occurred before. Only after gathering sufficient clinical information will the model draw a reasoned conclusion.
The idea of active clinical dialogue in medical AI is not new. In early 2024, Google DeepMind introduced AMIE (Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer) — a system specifically optimized for diagnostic conversations and history-taking, which in a study with patient actors outperformed primary care physicians on 30 out of 32 axes of clinical evaluation. However, AMIE remained a closed research model without public weights and without results on standard reproducible benchmarks. Baichuan-M3 follows the same path, but does so openly and with measurable results.
The model demonstrates three key capabilities that distinguish it from most predecessors.
- Active information gathering — M3 does not wait for the patient to volunteer all the details, but proactively asks the right diagnostic questions;
- The model uses multi-step reasoning, connecting disparate symptoms into a coherent diagnostic picture in exactly the same way that physicians do;
- Baichuan-M3 is equipped with an advanced medical hallucination control algorithm that actively verifies each claim to avoid generating potentially dangerous misinformation.
A Three-Stage Methodology for Teaching Clinical Thinking
Creating Baichuan-M3 is not a simple process of fine-tuning a language model on medical texts, but a complex process that mimics the training of real physicians. The researchers developed a unique three-stage methodology that allows the model to master various aspects of clinical practice without mutual conflict between tasks.
In the first stage, the team created highly specialized experts through Task-Specific Reinforcement Learning (TaskRL). One “doctor” was trained exclusively in clinical interviewing — the ability to collect symptoms and patient history. A second was specialized in health consulting and general medical recommendations. The third expert focused on fundamental medical reasoning and diagnostic logic. Each received rewards only for their narrow specialization, which made it possible to avoid the goal conflicts typical of multi-task learning.
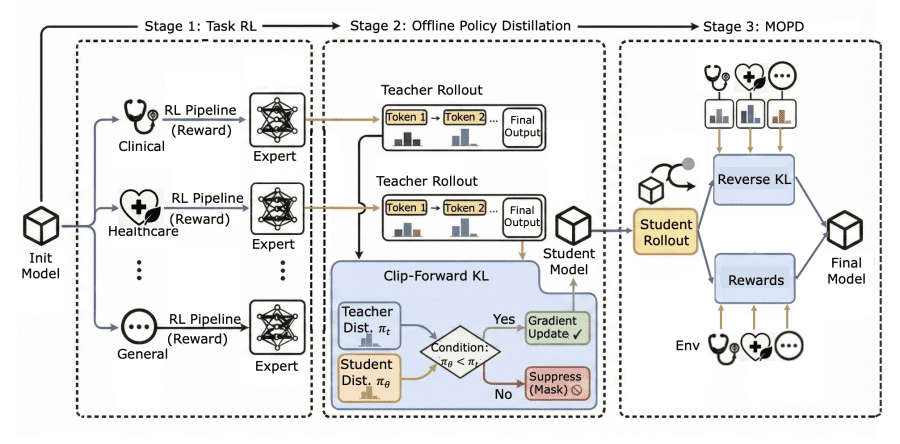
The second stage was a process of “knowledge merging” through Offline Policy Distillation, where a student model was created that could learn from all experts simultaneously. A special Clip-Forward-KL algorithm was applied here, which allows the model to adopt the best qualities of each teacher without losing previously learned skills. This is critically important, since standard approaches often lead to “forgetting” previous knowledge when acquiring new skills.
The final stage involved Multi-Teacher Online Policy Distillation (MOPD) — fine-tuning the merged model in a real clinical environment. At this stage, the model began receiving feedback from multiple teachers simultaneously, learning to balance various aspects of medical practice and adapt its behavior to specific clinical scenarios.
The SPAR Algorithm: Step-by-Step Refinement of Medical Dialogue
To train clinical interviewing skills, the researchers developed the SPAR algorithm (Step-Penalized Advantage with Relative baseline), which differs fundamentally from traditional approaches. While ordinary reinforcement learning methods evaluate a medical dialogue as a whole — as good or bad — SPAR analyzes the effectiveness of each individual turn.
The algorithm operates in two phases, creating a natural curriculum. The first phase focuses on correcting critical errors — repeated questions, violations of logical sequence, incorrect medical claims. The second phase handles the fine-tuning of communication style and professionalism, teaching the model delicacy when dealing with sensitive topics and precision in medical terminology.
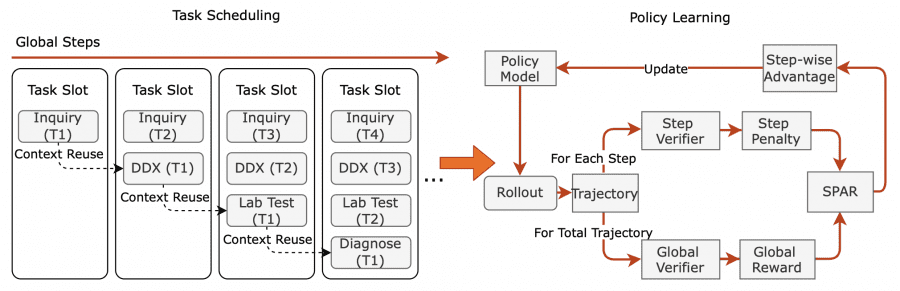
This approach allows the model to precisely understand which specific phrases in the dialogue contributed to a successful diagnosis and which led to problems or confusion. This creates far more precise training feedback compared to global assessments of consultation effectiveness.
Fact-Aware Reinforcement Learning Against Hallucinations
One of the most serious problems with modern medical AI is the tendency to generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect claims. In medicine, such “hallucinations” can have fatal consequences, which is why Baichuan-M3 is equipped with an advanced Fact-Aware Reinforcement Learning algorithm.
The algorithm works as a thorough real-time fact-checker. Each model response is automatically broken down into individual medical claims — from symptoms and diagnoses to treatment recommendations. Each claim is then verified through a search of authoritative medical sources and databases. Finally, the model receives differentiated feedback: rewards for verified facts and penalties for inaccuracies. To evaluate this technology, the authors use the HealthBench-Hallu metric — an approach in which long responses are broken down into atomic medical claims and each one is independently verified against authoritative sources.
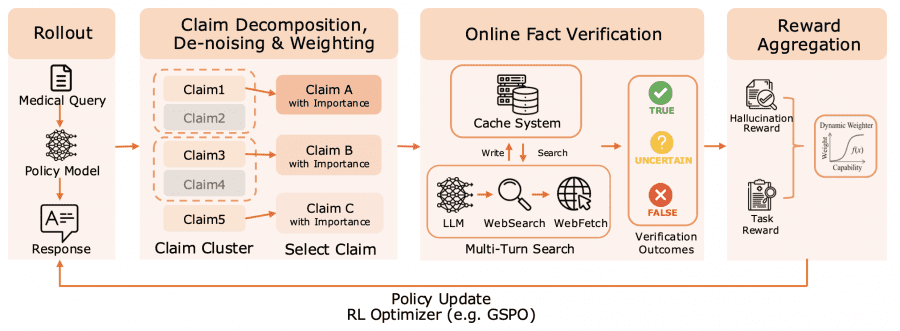
A key feature of the algorithm is that it accounts for the clinical importance of each claim. An error in diagnosis or treatment prescription will incur a significantly larger penalty than an inaccuracy in general healthy lifestyle recommendations. This helps the model focus on the most critically important aspects of medical practice.
Impressive Clinical Trial Results
The team tested Baichuan-M3 on several rigorous benchmarks, including the specially created ScanBench — a physician consultation simulator. This test reproduces the full cycle of a medical consultation, guiding the model through all stages: from the initial patient interview and history-taking to ordering necessary tests and delivering a final diagnosis.
On the critical clinical inquiry stage, M3 scored 74.9 points, significantly outpacing GPT-5.2-High with 62.5 points and a human physician with 54.6 points. Particularly striking was the model’s ability in safe medical stratification — identifying “red flags” and critical symptoms requiring immediate attention. Here M3 demonstrated a score of 75.8 points against 48.3 for the next best model and 40.1 for human physicians.
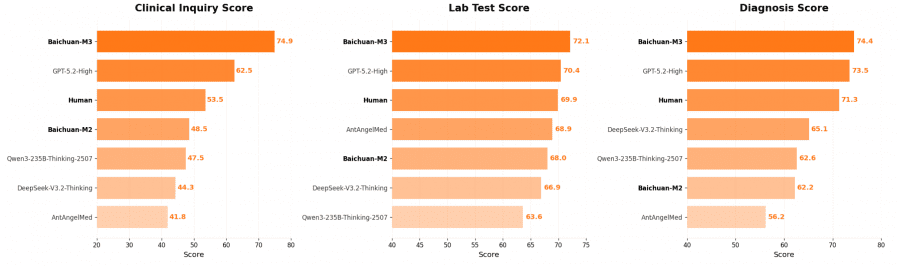
On the authoritative HealthBench medical benchmark, the model scored 65.1 points, surpassing GPT-5.2-High with 63.3. The results on the challenging HealthBench-Hard version are particularly impressive, where M3 achieved 44.4 points against 42.0 for GPT-5.2-High. Meanwhile, the medical hallucination rate was just 3.5% — significantly lower than competitors. This means M3 is simultaneously more accurate in diagnosis and safer to use.
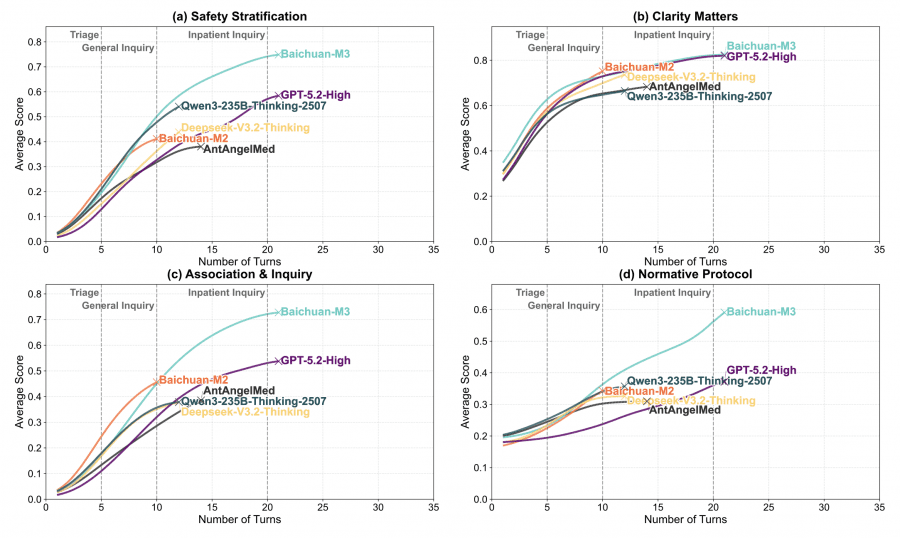
Particularly interesting was the analysis of model effectiveness as a function of dialogue length. While simple medical AI models lose focus after a few questions, Baichuan-M3 demonstrates a steady increase in effectiveness. In long consultations, the model shows almost a twofold advantage in the “Association & Inquiry” category, achieving high results where general models like Deepseek and Qwen fall significantly behind.
Efficient Inference
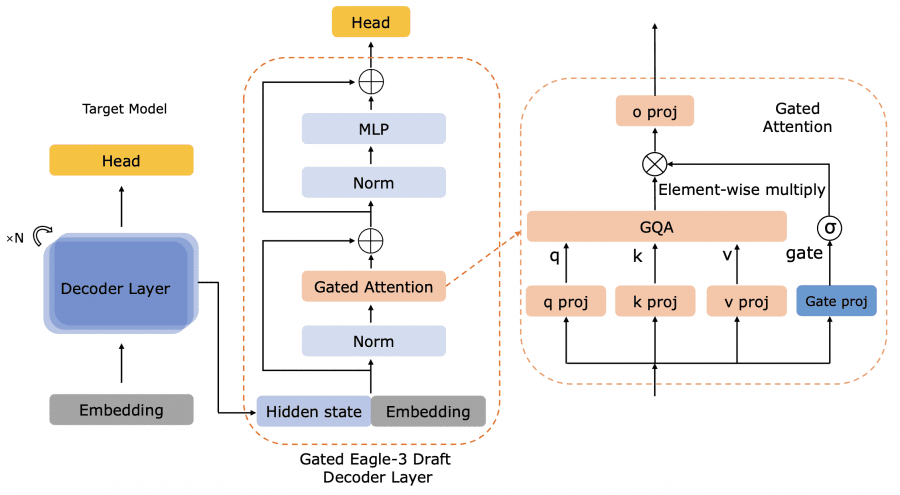
Recognizing that even the most advanced model is useless without the possibility of efficient deployment, the team proposed several optimizations. The Gated Eagle-3 algorithm is an improved version of speculative decoding that accelerates the generation of medical responses by 12% compared to the baseline Eagle-3 implementation. The Gated-Attention module provides dynamic and controlled regulation of information exchange between different components of the model. In parallel, a special INT4 quantization technique with self-generated calibration for Mixture-of-Experts was developed, allowing the model to be compressed without loss of diagnostic accuracy.
Limitations of the Current Version and Development Plans
The current version of Baichuan-M3 works exclusively with text-based episodic scenarios, meaning it is unable to conduct long-term medical monitoring of patients or analyze images such as X-rays or MRIs. The development team is already planning to address these limitations in future versions, adding multimodal capabilities and expanding the ability to work with long context for maintaining patient medical records.
Impact on the Future of Medicine
The direction in which Baichuan-M3 is moving is not simply a passive reference book of medical knowledge, but an active participant in the diagnostic process. This is especially critical in the context of the global shortage of medical personnel, where such models can significantly improve the quality of primary medical care.
The decision to make a significant part of the project open-source creates unique opportunities for the medical community. Researchers around the world gain access to cutting-edge technologies for developing specialized solutions adapted to the characteristics of national healthcare systems, local medical protocols, and the specific needs of different patient groups.
The research demonstrates a fundamental paradigm shift: the future of medical AI lies not in creating ever more sophisticated search systems for medical databases, but in precisely modeling the physician’s thought process itself. Baichuan-M3 shows that artificial intelligence can master not only medical knowledge, but also the art of applying it in complex clinical situations. The project’s main achievements include:
- Proactive clinical dialogue management — the model actively gathers medical history, asking the right questions in the right sequence
- Reliable medical information control — the fact-checking technology minimizes the risk of dangerous hallucinations
The real superiority of Baichuan-M3 over its predecessors comes from three factors simultaneously. Relative to its own predecessor Baichuan-M2, the progress is obvious: +28 points on HealthBench-Hard and a twofold reduction in hallucinations. Relative to GPT-5.2-High, the advantage is more modest in numbers, but fundamental in terms of conditions — Baichuan-M3 is open under the commercial Apache 2.0 license, while GPT-5.2 cannot be deployed locally. Relative to Google’s AMIE — a system that already demonstrated superiority over physicians in dialogic inquiry back in 2024 — direct comparison is impossible: Google has not published AMIE’s results on HealthBench, and AMIE itself remains closed. Baichuan-M3 is the first model of this class that can be downloaded, deployed, and independently verified, which in itself changes the rules of the game for the medical community.