Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have developed a technology that combines wireless sensing and artificial intelligence to detect medication errors without the need for physical contact. This device will help reduce the number of hospitalizations and health care costs, does not require constant monitoring of the patient and measurement of any parameters. The work was published in the Nature Medicine journal.
How does it work?
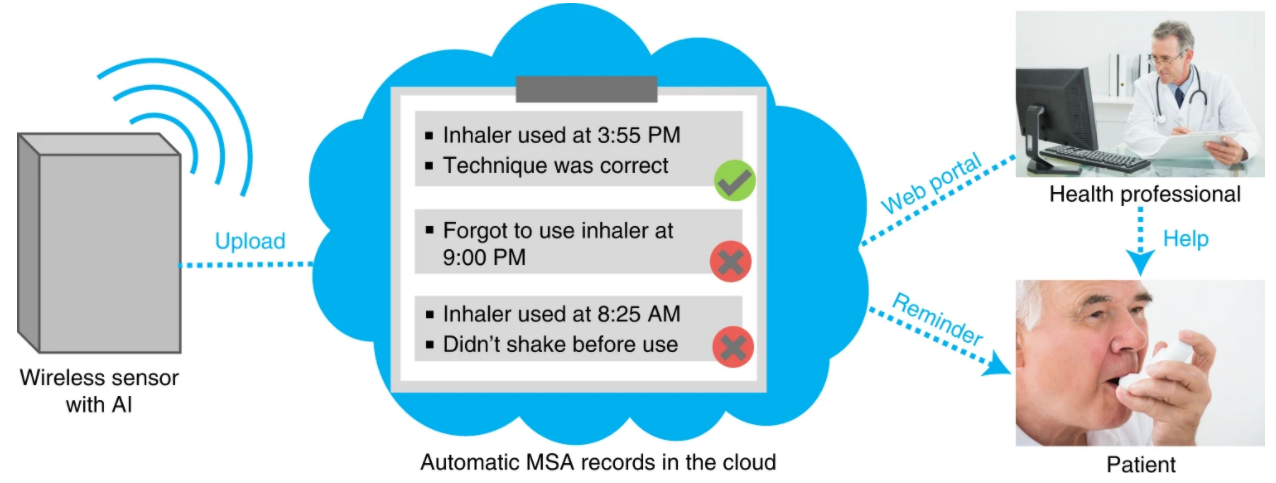
The developed system includes a wall-mounted Wi-Fi-type module (transmits signals in the Wi-Fi frequency range using the frequency-modulated continuous-wave method) installed in the patient’s home. The device emits very low-power radio waves. When a person moves, the waves are modulated and reflected in the sensor.

Each unique movement creates a corresponding pattern of modulated radio waves, for which the team has developed a neural network. First of all, artificial intelligence examines specific movements that indicate the use of drug delivery vehicles. Next, the neural network analyses the actions associated with the technique of using medications. The database for the neural network consists of examples of movements that indicate the usage of an inhaler or insulin pen, and examples of movements that correspond to common activities: cooking, typing texts or interacting with different objects. Through repetition and reinforcement, the neural network successfully recognized 96% of pen insertion and 99% of inhaler use. Moreover, the system can mark anomalies at any stage. For example, a neuron net can define whether the patient holds the insulin pen for five seconds instead of the prescribed 10 seconds. Information is transmitted over the Internet directly to a person and added to his medical record. The patient’s attending doctor will also be able to access these records through the web portal. In the case of errors in taking medications, a scheme and technique can be rapidly corrected. The researchers note that their system could be adapted to other medications as well. All that is required is to retrain the neural network.
In summary, a team of researchers has developed an artificial intelligence system that successfully tracks medication intake. The use of wireless technologies allows monitoring in a passive mode for the patient and reduces the burden on medical personnel. The accuracy of the results obtained demonstrates the high potential of using the device in the future.